Specialist dressing materials from ZARYS – professional solutions for medical personnel to treat various wound types
Specialist dressing materials are advanced solutions for treating various wound types. These modern products are used for both acute and chronic wounds, enhancing patient comfort while speeding up the healing process.
They feature advanced exudate management technology and create the ideal moisture environment for tissue regeneration. These dressings provide absorbent, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, or hemostatic benefits, depending on the wound needs.
Available as foam dressings, mesh dressings, alginate dressings, hydrocolloid dressings, hydrogel dressings, hydrofiber dressings, and tracheostomy dressings.
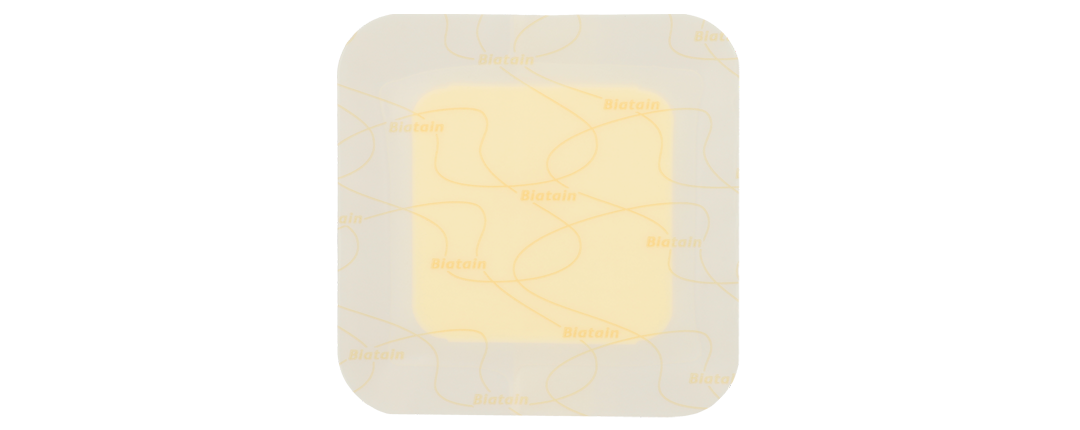
Foam Dressings
Made of hydrophilic polyurethane foam or absorbent polymer.
They have a porous structure that absorbs wound exudate. Flexible and conforming to body contours, they maintain appropriate wound moisture.
The waterproof, vapor-permeable outer layer protects against bacteria and viruses. Enriched with active substances (silver, methylene blue, or gentian violet), they combat microorganisms, bacteria, and fungi.
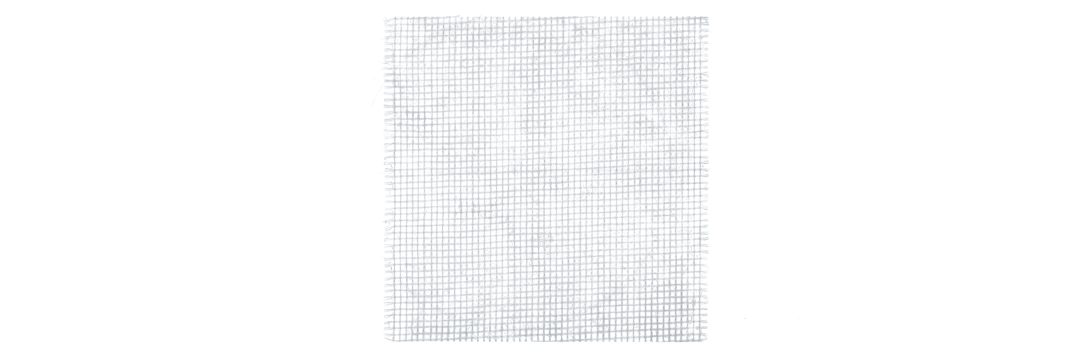
Mesh Dressings
Made from cotton or synthetic material, these dressings are impregnated with active substances (silver ions, silver sulfadiazine).
Their large openings prevent fluid accumulation and facilitate drainage to the secondary dressing.
They provide a lipid film that makes dressing changes painless and prevents irritation to granulation tissue.
Alginate Dressings
Made from calcium alginate, these dressings have absorbent and emulsifying properties. They transform from a fibrous structure into a gel when in contact with the wound, perfectly conforming to its shape.
They provide hemostatic benefits and maintain a moist healing environment. Since they don’t adhere to wounds, they allow for painless changes.
These dressings require an additional secondary dressing, which should be selected based on the amount of wound exudate.

Superabsorbent Dressings
Their primary function is to maintain proper moisture in the wound while preventing maceration and skin damage from excessive exudate.
These dressings serve as secondary absorbent layers and provide additional support for hydrofibers and polyurethanes in cases of heavy wound drainage.
With their superior absorption capacity, they reduce the frequency of necessary dressing changes

Hydrocolloid Dressings
Made from hydrocolloids — biopolymers with absorbent properties.
These dressings absorb excess exudate and lock it in a gel form, cleansing the wound. They prevent excessive wound drying by maintaining proper moisture levels.
They easily conform to body contours and can be trimmed to the appropriate size as needed.
Hydrogel Dressings
Made from a three-dimensional network of hydrophobic polymers. Their structure contains highly hydrated hydrophilic groups, consisting of 92-95% water.
Used in the initial stage of wound treatment to assist with cleansing. They release moisture into the wound, maintaining a moist environment that promotes granulation and epithelial regeneration.

Hydrofiber Dressings
Made from sodium carboxymethyl cellulose.
When in contact with wound exudate, they transform into a transparent gel that fills the wound and absorbs drainage.
Used for deep wound drainage, they prevent skin maceration. To enhance their absorption properties and extend wear time, it’s recommended to use them in combination with hydrocolloid or alginate dressings.

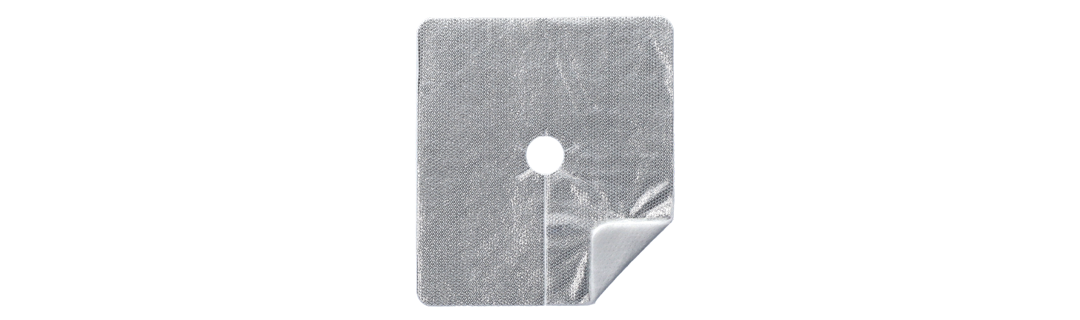
Tracheostomy Tube Dressings
Specialized dressings with an opening specifically designed to fit around tracheostomy tubes.
Thanks to their special coatings, these dressings don’t adhere to wounds or cause pain when in contact with the patient’s skin. They enhance both healing time and the overall recovery process. These dressings don’t cause irritation during use.